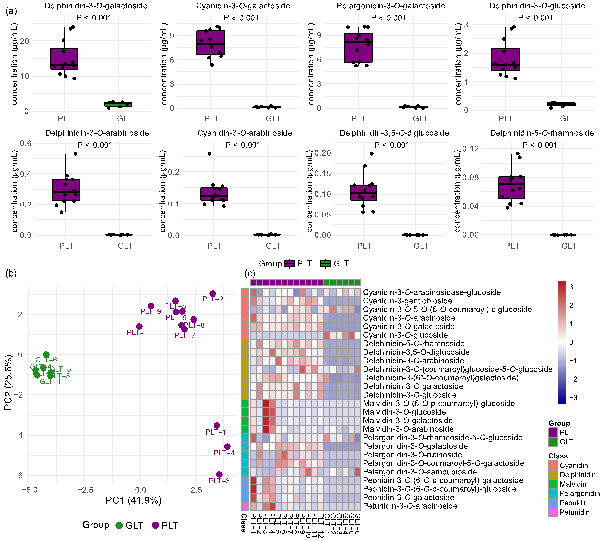
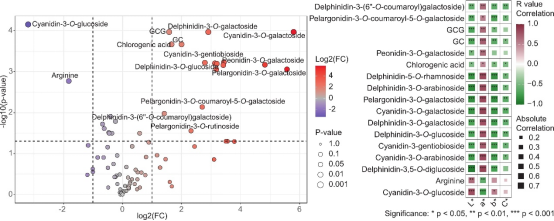
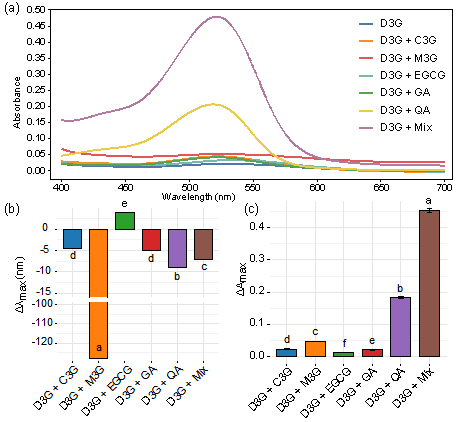
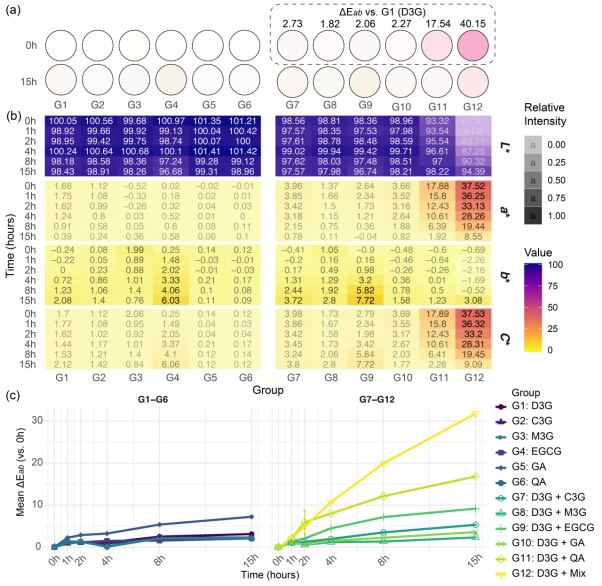
Purple leaf tea (PLT) is gaining attention for its vibrant color and potential health benefits. This study focuses on the critical role of co-pigmentation in dictating the vibrant color and stability of its anthocyanins. PLT infusions exhibit a distinct reddish-purple hue, contained approximately 10.3-fold higher total anthocyanin levels (average 34.33 μg/mL) than green leaf tea as determined by chromatography, with delphinidin-3-O-galactoside (D3G; average 15.02 μg/mL) and cyanidin-3-O-galactoside (average 7.97 μg/mL) being dominant. Co-pigments markedly intensified D3G's coloration. For instance, gallic acid and quinic acid induced hypsochromic shifts, decreasing λmax by 7–9 nm. Thermally (80 °C, 15 h), gallic acid significantly improved D3G stability (21.0 % retention), correlating with strong docking affinity (−3.605 kcal/mol) via H-bonds and π-π stacking. Conversely, epigallocatechin gallate dramatically reduced D3G stability (1.7 % retention). These specific molecular interactions critically influence PLT's anthocyanin color expression and thermal stability, offering key insights for quality optimization.
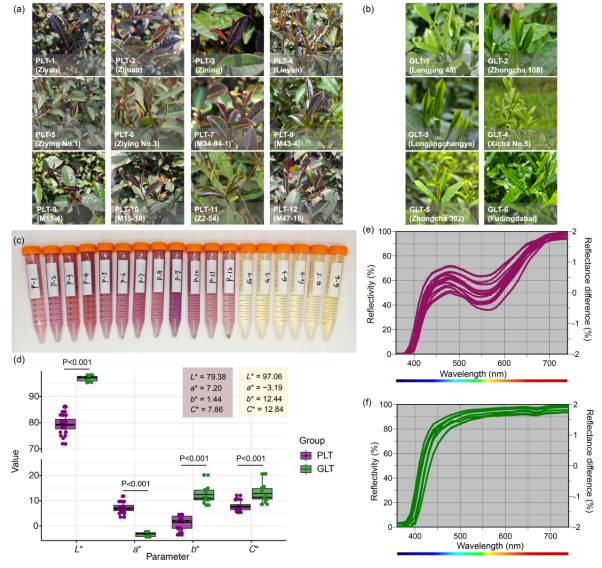
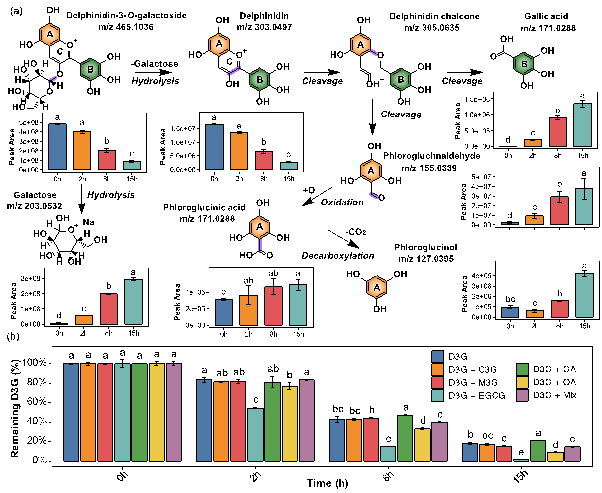
图6. D3G的热降解及添加共色素的影响。 (a)D3G的热降解途径和(b)共色素组中D3G的定量保留率。 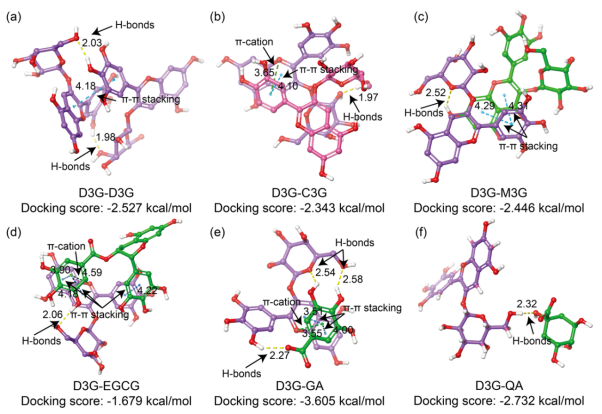

相互作用的颜色呈现如下:氢键(黄色虚线)、π-π相互作用(蓝色虚线)、π-阳离子(绿色虚线)。
作者:中国农业科学院茶叶研究所 杨高中
审稿:安徽农业大学 张梁 教授
来源: 中国茶叶学会
内容资源由项目单位提供

 科普中国公众号
科普中国公众号
 科普中国微博
科普中国微博

 帮助
帮助
 中国茶叶学会
中国茶叶学会